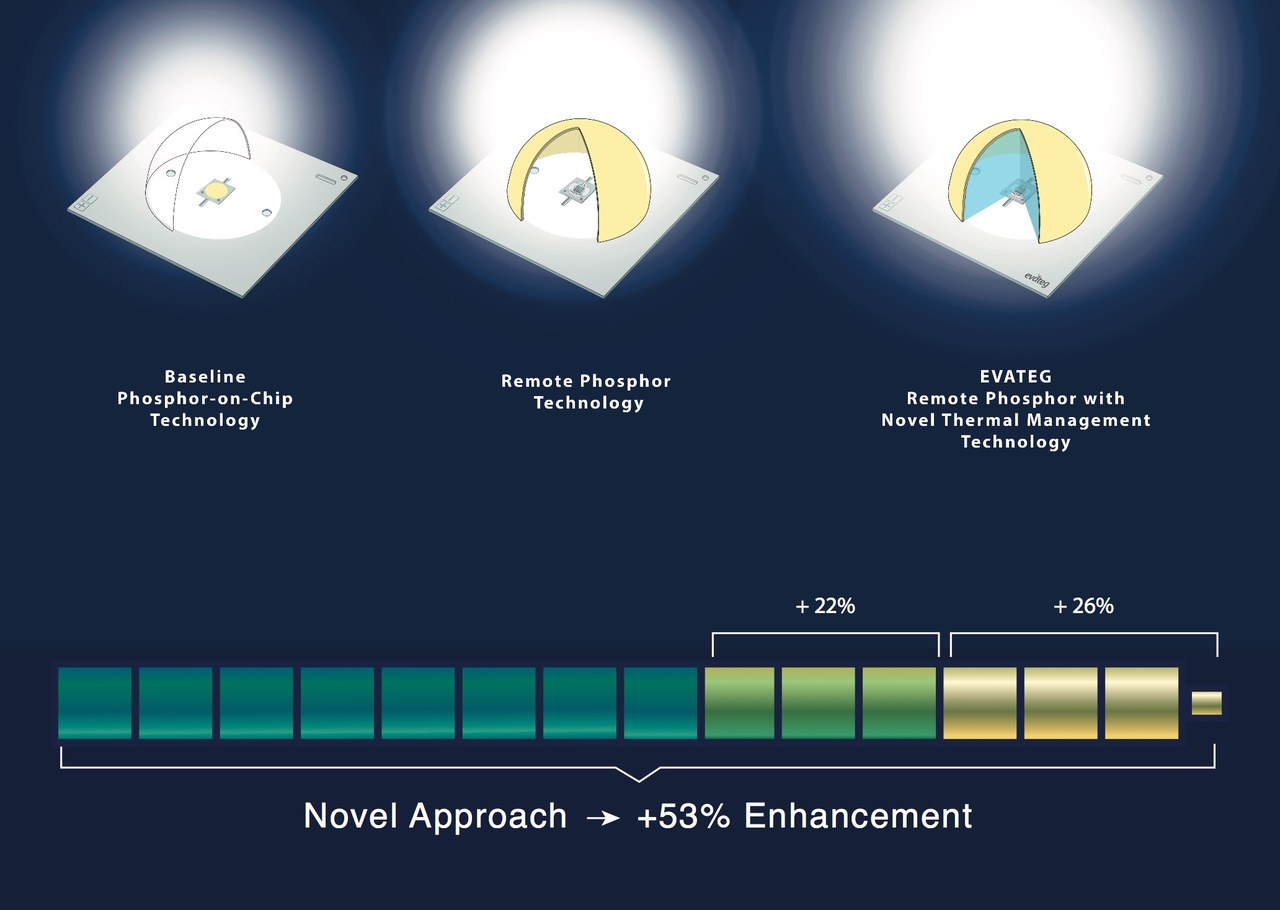
Innovation Extends the Lumen Extraction Limits of RGB and White LEDs in Excess of 53%
EVATEG Energy Efficient Electronics and Lighting Technologies Center recently demonstrated a new optical extraction technology for RGB and phosphor coated LEDs to extend the limits over 53%.
This new technology has been studied over the last 6 years with a group of researchers under Dr. Mehmet Arik of Ozyegin University who has over 17 years of experience including 11 years at GE Global Research Laboratories in New York, USA. While conventional LED packages consist of silicone-phosphor mixture over the chip, causing some significant optical losses due to refractive index mismatching, local heat transfer as well as local phosphor heating issues; EVATEG’s novel idea enhances the light extraction by appliying the phosphor away from the chip with remote coating under glass dome and decreases the junction temperature with optothermal liquid cooling technologies. The system an extensive comparison between the baseline (conventional LED packages) with air filled, fully silicone cured and optothermal fluid filled seperately has shown an increase over the lumen output as %23, %40 and %53 over the baseline respectively.
Furthermore, this novel idea brings the following key advantages over conventional approaches:
- Provides an effective cooling of LED light engines abating local temperature non-uniformities
- Simplifies complex lighting system designs
- Reduces the thermal resistance between the chip and heat sink significantly and leads to high lumen extraction
- Key enabler technology for advanced IoT features for lighting systems
- Lowers the junction temperature with an effective cooling of chip and phosphor while increasing the lumen output and lifetime
- Higher conversion efficiency in phosphor with decreasing temperature
- Eliminates color shifts due to temperature overshoots
- Enables a better refractive index matching reducing optical losses