Blue Wavelengths of LED Light Negatively Affect Milk Quality
Matt Hayes, managing editor and social media officer for the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and Alina Stelick, research support specialist in the Department of Food Science, report at the Cornell Chronicle of June 8th, 2016 that Cornell researchers in the Department of Food Science found exposure to light-emitting diode (LED) sources for even a few hours degrades the perceived quality of milk more so than the microbial content that naturally accumulates over time. Their study determined milk remained at high-quality for two weeks when shielded from LED exposure, and consumers overwhelmingly preferred the older, shielded milk over fresh milk stored in a typical container that had been exposed to LED light for as little as four hours.
As sellers adopt these light-efficient energy sources in dairy cases and point-of-sale locations, merchants might unwittingly sabotage the product they are trying to sell.
“For some reason we love to look across the store and see this glowing case of milk that’s shining bright,” said Robin Dando, senior author on the paper and assistant professor in the Department of Food Science. “It’s attractive to look at, but we might actually be damaging the quality of the product.”
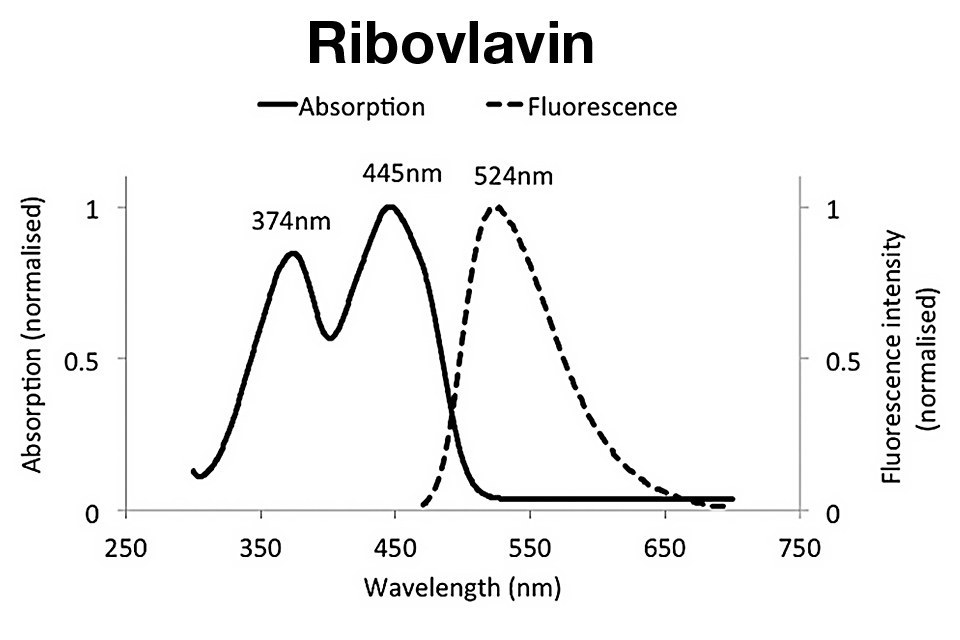
It’s well understood that milk sensory quality and nutritional content are adversely affected by exposure to the sun and artificial light sources. Riboflavin and other photosensitive components in milk are activated when struck by light energy, releasing a cascade of electrons that can degrade proteins and oxidize fats.
The resulting taste is commonly described as that of cardboard or plastic. All current popular milk packaging allows for certain light exposure to occur; even opaque plastic jugs have potential to compromise the highest quality milks by allowing off-flavors to develop.
For the study, consumers rated skim and 2 percent milk that differed based on light exposure. Some of the milk was kept shielded from all light for 14 days, while a one-day old batch was exposed to real-world LED lighting found in stores for four hours.
Overall, the data suggests consumer preference of skim and 2 percent milk is more profoundly influenced by exposure to LED lighting than by the storage time. The light exposure effects were so powerfully negative that the “near code/near expiration date” sample was preferred in every case to the fresh sample regardless of microbial defects.
“Milk drinkers want the freshest, highest quality milk they can get,” said Nicole Martin, the study’s lead author and supervisor of Cornell’s Milk Quality Improvement Program laboratory. “For most consumers the idea of freshness is in inverse relationship to the expiration date on the package. This study shows that light exposure is a much greater factor explaining deteriorating milk quality than even age.”
LED lighting produces a pattern of wavelength that differs from the fluorescent bulbs used to illuminate display cases. LEDs typically emit in the blue spectrum, around 460 nanometers, and produce a broader emission peak than fluorescents. That peak in LED light is near the narrow band where riboflavin absorbs light, a fact the researchers surmise could be selectively destroying the nutrient and damaging the perceived quality of the milk.
“We found that without LED exposure, most pasteurized milk remains at high quality for 14 days; importantly this study now provides new information that can be used to further improve the quality of milk, for example through light shielding packaging,” said co-author Martin Wiedmann, the Gellert Family Professor in Food Safety.
LEDs are becoming more common as stores install the lights to boost energy-efficiency. The researchers suggest manufacturers could turn to better light-blocking packaging to reduce the damaging effect of all light types.
The study, “Exposure of fluid milk to LED light negatively affects consumer perception and alters underlying sensory properties,” was selected as an editor’s choice in the June edition of the Journal of Dairy Science. Other authors include Nancy Carey; Steven Murphy; David Kent; Jae Bang; and Tim Stubbs.